Introduction
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a wide range of storage solutions to cater to the diverse needs of businesses and developers. Two popular options are Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) and Amazon Elastic File System (EFS). While both provide storage capabilities within the AWS ecosystem, they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. In this blog post, we will explore the key differences between AWS EBS and AWS EFS to help you make an informed choice for your specific use case.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS)
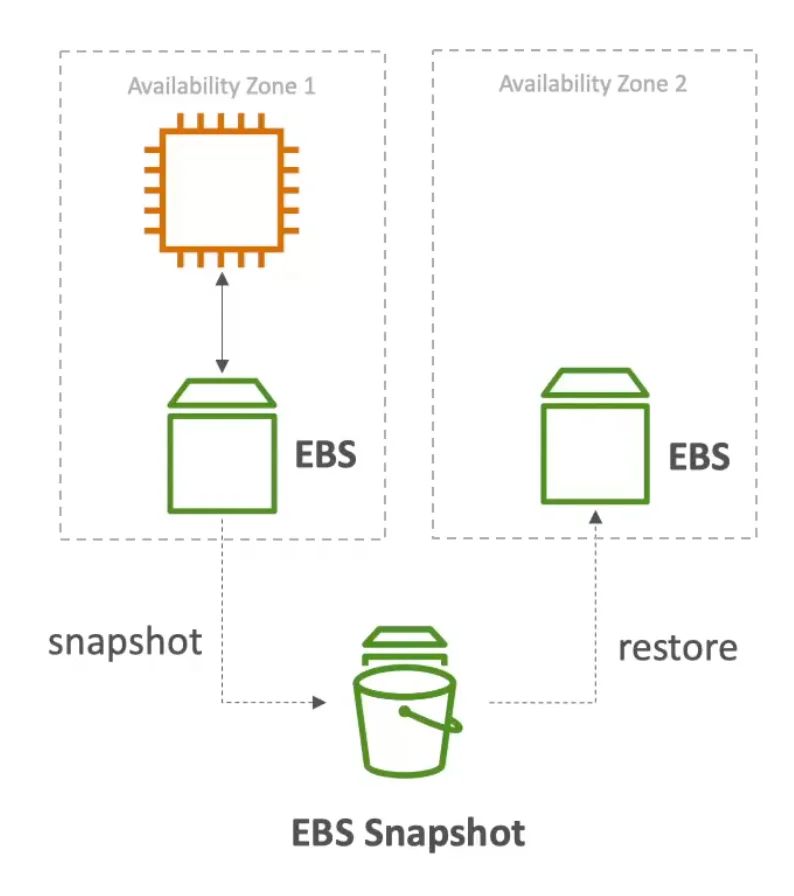
Here are some of the main characteristics and use cases of AWS EBS.
Block Storage
EBS provides block storage, which means it is best suited for scenarios where you need to store data at the block level, such as databases and applications that require direct access to disk devices.
Low-Latency Performance
EBS volumes offer low-latency, high-throughput performance, making them ideal for I/O-intensive workloads where rapid data access is crucial.
Data Persistence
EBS volumes are persistent, meaning the data stored on them remains intact even when the associated EC2 instance is stopped or terminated. This is useful for maintaining critical data.
Availability and Redundancy
EBS volumes can be replicated within a specific
Availability Zone (AZ) for redundancy, but they are not natively designed for cross-AZ or cross-region redundancy. For cross-AZ redundancy, you need to set up additional configurations.
Cost
You pay for the provisioned capacity of the EBS volume, regardless of whether it is in use or not. This can make it cost-effective for certain use cases but might require careful capacity planning.
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS)
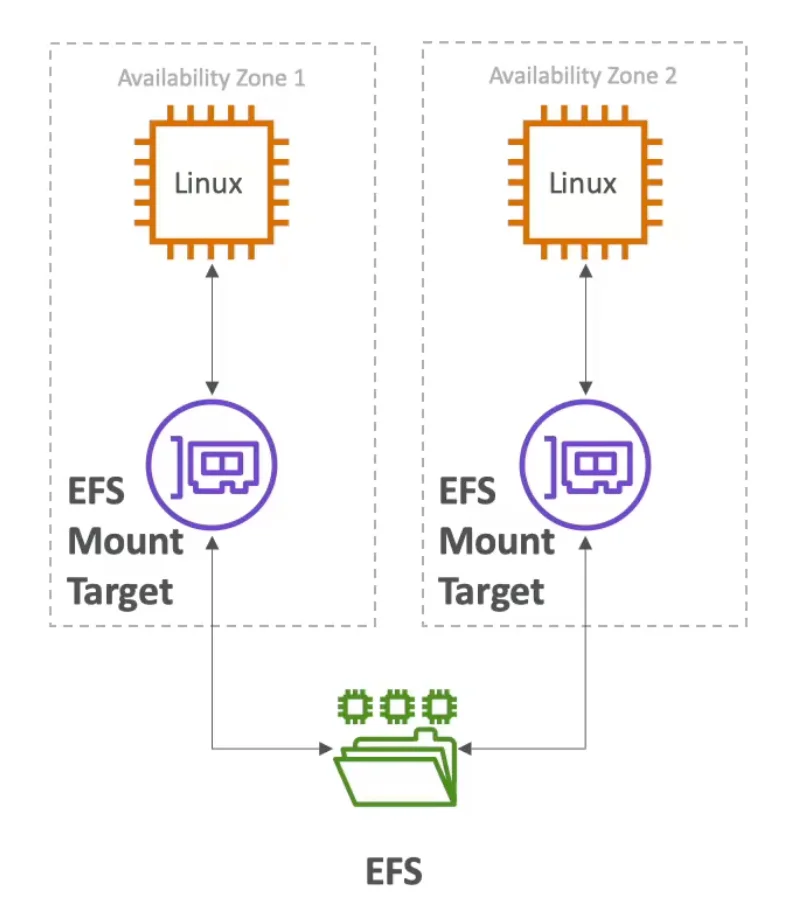
Here are the key attributes and use cases of AWS EFS:
File Storage
EFS offers file-level storage, making it suitable for scenarios where multiple instances need shared access to the same data, such as web applications, content management systems, and shared repositories.
Scalability
EFS is designed to scale automatically as your storage needs grow. It can handle a dynamic number of EC2 instances concurrently, making it a great choice for applications with varying workloads.
Cross-AZ and Cross-Region
EFS provides built-in redundancy and can be accessed across multiple Availability Zones and even across regions. This ensures high availability and disaster recovery capabilities.
Pay-as-You-Go
With EFS, you pay for the storage capacity you use, making it a cost-effective option for applications with fluctuating storage requirements.
Simplified Management
EFS takes care of the underlying infrastructure and scaling, allowing you to focus on your applications without worrying about managing storage hardware.
Choosing Between EBS and EFS
To decide between AWS EBS and AWS EFS, consider the following factors:
Use Case
Determine whether your application requires block-level storage (EBS) or file-level storage (EFS).
Performance Requirements
Assess your performance needs. EBS is often preferred for high-performance workloads, while EFS offers good performance for a wide range of applications.
Scalability
Consider whether your storage needs are likely to scale over time. EFS is designed for easy scalability.
Availability and Redundancy
If high availability and redundancy are crucial, EFS may be a better choice due to its built-in cross-AZ and cross-region capabilities.
Cost
Evaluate your budget and cost considerations. EBS charges are based on provisioned capacity, while EFS charges are based on actual usage.
Conclusion
In summary, AWS EBS and AWS EFS are both valuable storage services within the AWS ecosystem, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. EBS is ideal for block-level storage with high-performance requirements and provides data persistence within a single Availability Zone. On the other hand, EFS is designed for scalable file-level storage. Your choice between the two should be based on your specific use case and requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing your AWS storage strategy and ensuring the best performance and cost-efficiency for your applications.


