In previous blog, we discussed about the basics of Sentiment Analysis and load the raw dataset which is IMDb movie reviews. In this blog, we will discuss about text vectorization and how to use it in Sentiment Analysis.
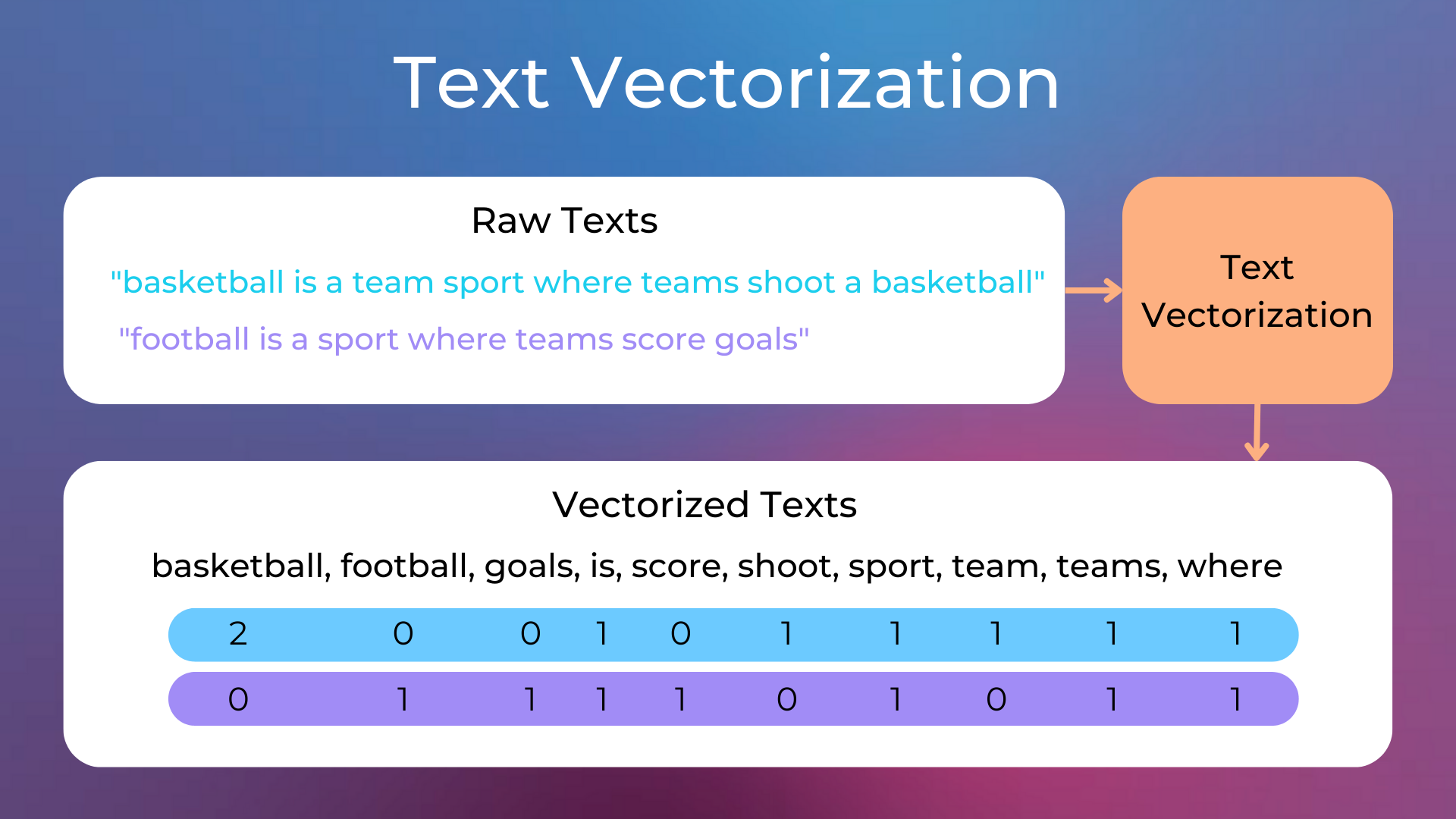
Text Vectorization Methods
Before train the model, we need to convert the text data into numerical data. Text representation is the process of converting text data into a numerical form that can be used for machine learning tasks. There are several ways to represent text data, such as Bag-of-Words, TF-IDF, and Word Embeddings.
Bag-of-Words (BoW)
Bag-of-Words (BoW) is a method of text representation that converts text into a word frequency vector. In this representation, the text is treated as a “bag” containing all the words, without considering their order and grammatical structure. The number of times each word appears in the text is recorded, forming a vector. This method ignores the order and context of words but is simple and easy to implement.
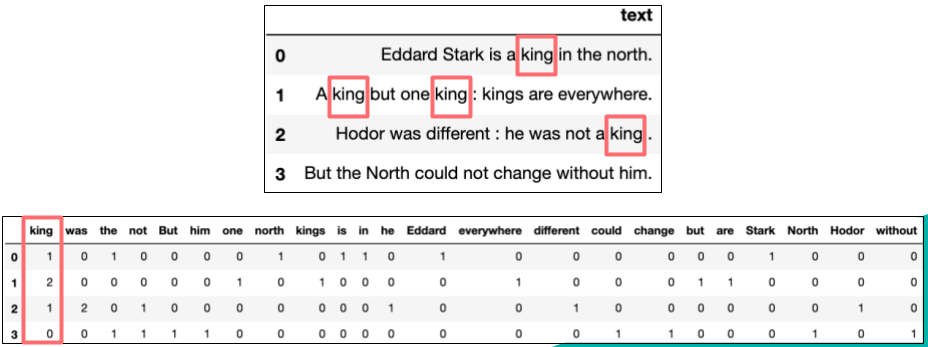
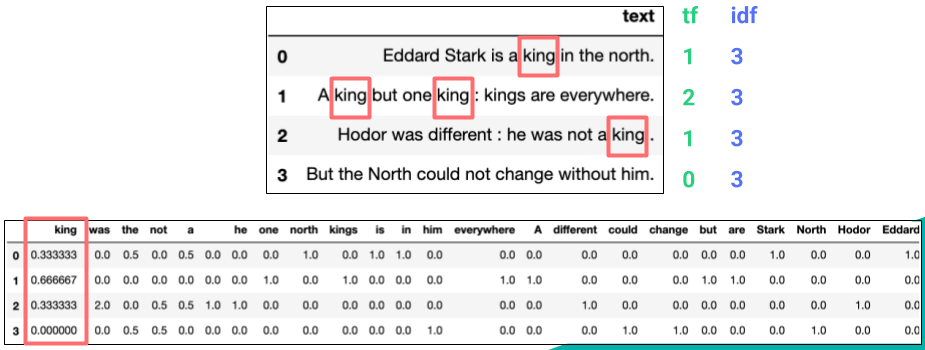
TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency)
TF-IDF is a statistical method used to evaluate the importance of a word in a document collection or corpus. It consists of two parts:
Term Frequency (TF): The frequency of a word in a document.
Inverse Document Frequency (IDF): The inverse of the document frequency, which measures the general importance of a word across all documents. IDF is calculated by taking the logarithm of the total number of documents divided by the number of documents containing the word.
The TF-IDF value is the product of TF and IDF, used to measure the importance of a word in a document. The higher the TF-IDF value, the more important the word is in the document.
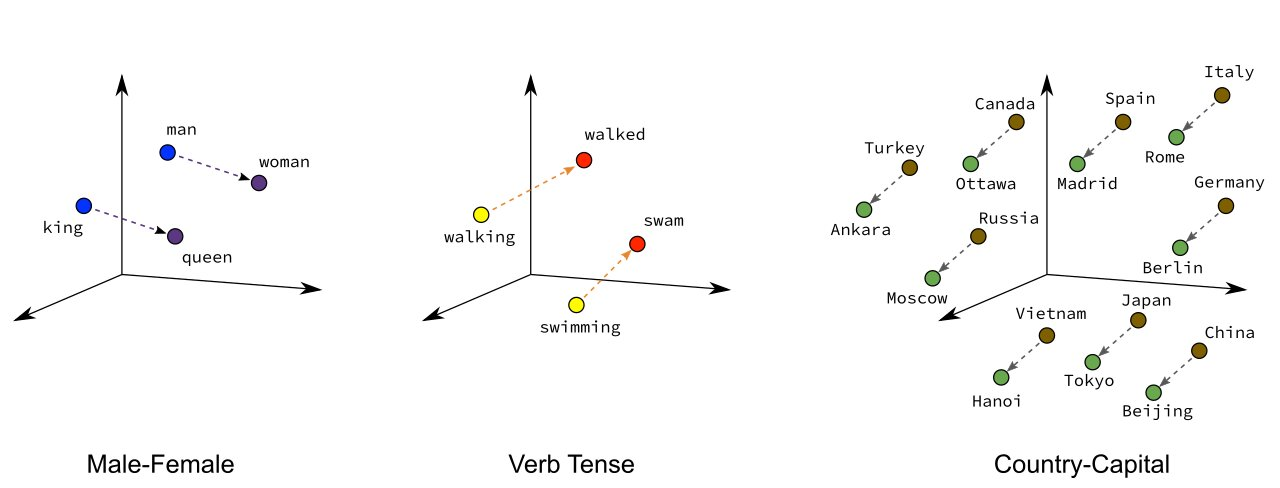
Word Embeddings
Word Embedding is a technique that represents words as dense vectors. Unlike traditional Bag-of-Words and TF-IDF methods, Word Embedding captures semantic relationships between words. Through training, these vectors can represent words in a vector space, where words with similar meanings are closer to each other in the vector space. The main advantages of Word Embedding include:
Semantic Capture: It can capture semantic relationships between words, for example, the distance between “king” and “queen” in the vector space will be closer than the distance between “king” and “apple”.
Dimensionality Reduction: Compared to high-dimensional One-Hot encoding, Word Embedding typically uses lower-dimensional vectors to represent words.
Context Awareness: Some advanced Word Embedding techniques (such as BERT and GPT) can capture the meaning of words in different contexts.
In deep learning models, Word Embedding is usually used as an input layer to convert text data into numerical vectors, making it easier for neural networks to process.
Text Vectorization
In this section, we will discuss about different text vectorization techniques and how to use them in Sentiment Analysis. This method TextVectorization layer in TensorFlow is similar to Bag-of-Words because it converts text into sequences of integer encodings, without considering the order of words. Unlike traditional Bag-of-Words and TF-IDF, the TextVectorization layer is implemented directly in TensorFlow, making it easy to integrate with deep learning models.
Create TextVectorization Layer
Below is the code to covert the text data into numerical data using TextVectorization layer in TensorFlow:
1 | import tensorflow as tf |
In the above code, we first import the necessary libraries and load the configuration file. We then define a function create_text_vectorization_layer which takes the raw training dataset as input and returns the TextVectorization layer.
The TextVectorization layer is initialized with the standardize parameter set to lower_and_strip_punctuation, which converts all text to lowercase and removes any punctuation. The max_tokens parameter is set to config.max_features, which is the maximum number of unique words to keep in the vocabulary. The output_mode parameter is set to int, which means that the output will be integer indices representing the words in the vocabulary. The output_sequence_length parameter is set to config.sequence_length, which is the length of the output sequences.
We then adapt the vectorization layer to the training data using the adapt method. This method fits the vectorization layer to the vocabulary of the training data, which is used to encode the input text into integer sequences.
Vectorize Text Data
After that, we can use the TextVectorization layer to vectorize the text data. Core code as below:
1 | def vectorize_text(text, label, vectorize_layer): |
The above code defines two functions: vectorize_text and vectorize_dataset. The vectorize_text function takes the text data and label, and applies the TextVectorization layer to the text data. The vectorize_dataset function takes the raw dataset and the TextVectorization layer, and applies the vectorize_text function to each element in the dataset. The cache and prefetch methods are used to optimize the performance of the dataset.
The function vectorize_dataset returns the vectorized dataset, which can be used to train the model.
In next blog, we will talk about build a Sentiment Analysis model using TensorFlow and Keras, and using this vectorized dataset to train the model.


