In previous post, we have talk about the Text Vectorization which is the process of converting text data into numerical data. In this post, we will build a Sentiment Analysis model using Keras and Tensorflow libraries.
Neural Network
Before build the tensorflow model, let’s take a look the Neuron Network. The Neuron Network is a type of artificial neural network that is based on the structure of the human brain. It consists of layers of interconnected neurons, or nodes. Each neuron receives input from other neurons, processes it, and then passes the output to other neurons. The final output of the network is a prediction of the network’s input.
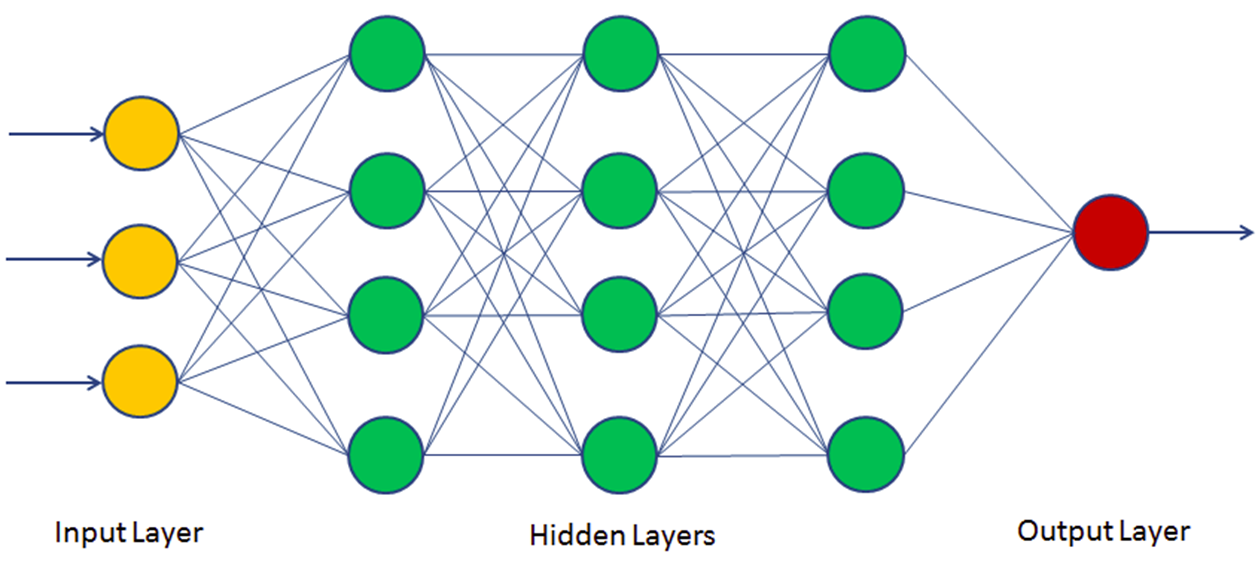
In the Neural Network, there are three layers, input, hidden, and output. The input layer receives the input data, the hidden layer processes the data, and the output layer produces the output. The hidden layer consists of multiple neurons, each with its own weights and biases. The weights and biases are adjusted during the training process to minimize the error between the predicted output and the actual output.
Sentiment Analysis Model
In the Sentiment Analysis model, we will use the Keras library to build the Tensorflow model. The Keras library is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Pytorch etc. It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation.
Below is the code to build the Sentiment Analysis model using Keras and Tensorflow libraries. We using Embedding, GlobalAveragePooling1D, Dense, Dropout layers to build the model.
1 | model = tf.keras.Sequential([ |
To better understand each layer’s purpose, let’s break it down into Chinese.
Sequential Model
Sequential是Keras中的一种模型,它是一种线性堆叠模型,即将多个层连接在一起。它可以将多个层作为一个整体来看待,并将其输出作为下一个层的输入。
Embedding Layer
Embedding层是一种用于将整数序列(通常是词汇表中的单词索引)转换为密集向量表示的层。它的作用是将离散的、高维度的输入(如单词索引)映射到连续的、低维度的向量空间中。
词嵌入:将词汇表中的每个单词映射到一个固定大小的向量。这些向量可以捕捉单词之间的语义关系,例如相似的单词在向量空间中会更接近。
降维:将高维度的输入(如词汇表中的单词索引)转换为低维度的向量表示,从而减少模型的参数数量和计算复杂度。
GlobalAveragePooling1D Layer
GlobalAveragePooling1D是Keras中的一种池化层,用于一维数据(如时间序列或文本数据)。它的作用是将输入的每个特征维度进行全局平均池化,从而将每个特征维度压缩为一个单一的值。
降维:通过计算每个特征维度的平均值,将输入的维度减少到一个单一的值。例如,如果输入是一个形状为(batch_size, steps, features)的张量,GlobalAveragePooling1D将输出一个形状为(batch_size, features)的张量。
特征压缩:通过全局平均池化,可以有效地压缩输入的特征,减少模型的参数数量和计算复杂度。
Dense Layer
Dense层是一种全连接层(fully connected layer),也称为密集层。它的作用是将输入的每个元素与该层的每个神经元进行连接,并应用线性变换和激活函数。
线性变换:对输入数据进行线性组合,即通过权重矩阵和偏置向量对输入进行加权求和。
激活函数:在完成线性变换后,应用激活函数(如ReLU、sigmoid、tanh等)以引入非线性特性,从而使神经网络能够学习和表示更复杂的函数。
Dropout Layer
Dropout层是一种正则化技术,用于防止神经网络过拟合。它的作用是在训练过程中随机地将一些神经元的输出设置为0,从而使得网络不会过度依赖于某些特定的神经元,增强了模型的泛化能力。
随机失活:在每次训练迭代中,Dropout层会随机选择一定比例的神经元(由参数rate指定,例如0.1表示10%的神经元),并将它们的输出设置为0。
减少过拟合:通过随机失活神经元,Dropout层可以减少神经网络对特定输入特征的依赖,从而防止模型在训练数据上过度拟合,提高模型在未见数据上的泛化能力。
Sigmoid Activation Function
Sigmoid激活函数是一种常用的激活函数,它将输入值压缩到0-1之间,并将输出解释为概率。
The summary() method is used to print the model architecture. It provides a summary of the layers in the model, including the number of parameters and the shape of the output.
So now, we have build the Sentiment Analysis model using Keras and Tensorflow libraries. In the next post, we will train the model and evaluate its performance.


