As artificial intelligence (AI) models, especially large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT series, have become increasingly sophisticated, a new role has emerged in the AI ecosystem: the Prompt Engineer. The term might sound technical or niche, but it’s actually pivotal to leveraging AI models effectively. Whether you’re interacting with AI in your personal or professional life, the quality of the interaction largely depends on how well the prompt is designed. This article will explore what a prompt engineer does, the best practices for writing effective prompts, and provide examples comparing outputs with and without a prompt engineer’s expertise.

What is a Prompt Engineer?
A Prompt Engineer is someone who specializes in crafting, refining, and optimizing prompts to ensure that AI models respond with the most relevant,accurate,and actionable information. The role requires a blend of creativity, technical understanding, and knowledge of the AI’s underlying model architecture.
In essence, the prompt engineer’s job is to “speak” the language of the AI model. Since AI models like GPT-3 or GPT-4 don’t “think” like humans, their responses depend heavily on how the question or task is framed. A prompt engineer ensures that the right context, constraints, and phrasing are in place to guide the model toward producing the most useful responses.
Why is Prompt Engineering Important?
While AI models are capable of generating human-like text and performing complex tasks, their outputs are highly sensitive to the structure of the prompt. The same AI model could provide vastly different answers depending on the way a question is asked. Prompt engineers understand this sensitivity and use it to maximize the effectiveness of the interaction with AI.
Here are some reasons why prompt engineering is important:
Maximizing output quality: Well-designed prompts improve the accuracy, relevance, and clarity of responses.
Reducing errors: By properly framing a prompt, prompt engineers can help reduce misunderstandings or irrelevant responses.
Efficiency: Instead of relying on trial and error to get useful responses, prompt engineers streamline the interaction process, saving time and resources.
Contextuality: A good prompt will provide the necessary context for the model, ensuring that the response is in line with the user’s expectations.
The Path of a Prompt Engineer
The process that a prompt engineer follows to ensure optimal results involves several stages. Each stage builds upon the last, leading to an iterative cycle that refines both the prompt and the AI’s output. Here’s a breakdown of the typical path of a prompt engineer:
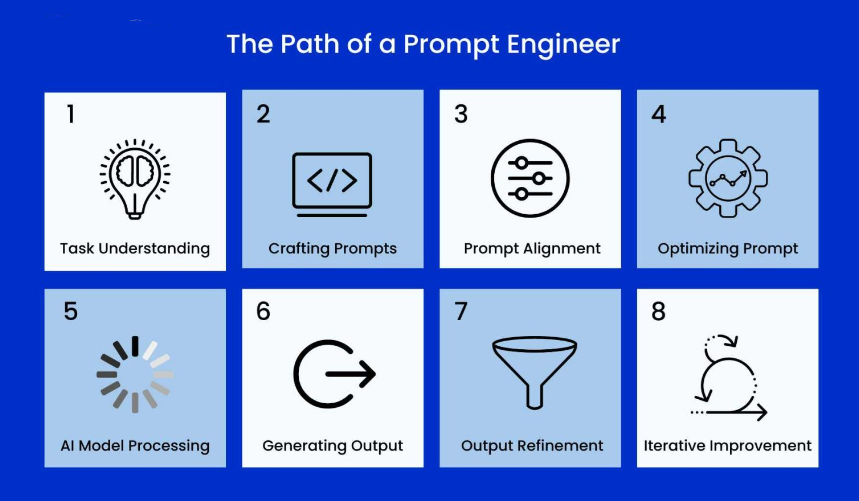
1.Task Understanding:
Before crafting any prompt, the first step is to fully understand the task at hand. This involves clarifying the user’s goal, determining the desired output format, and understanding the nuances of the request. A deep understanding of the problem ensures that the prompt engineer can craft a question or instruction that addresses all necessary aspects.
Example: If the task is to generate a poem, the prompt engineer will need to understand the tone, style, and subject matter required.
2.Crafting Prompts:
The next step is to craft the prompt. This involves framing the task clearly, with enough specificity to guide the AI toward the desired output. Crafting an effective prompt is not about asking a single question, but about providing the model with the right context, constraints, and direction.
Example: Instead of asking, “Write a poem,” a more specific prompt might be, “Write a rhyming poem about the beauty of autumn, focusing on imagery and feelings of nostalgia.”
3.Prompt Alignment:
At this stage, the prompt must be aligned with the intended outcome. This means considering the AI model’s strengths and limitations and ensuring that the prompt leads the AI to produce a response that fits the desired format, tone, and depth. The prompt should ensure the model understands the context of the task, as well as any constraints or preferences that need to be respected.
Example: For a technical article, aligning the prompt would involve ensuring the language model knows to prioritize clarity, accuracy, and technical precision.
4.Optimizing Prompt:
After alignment, the prompt may need further refinement. This step involves fine-tuning the wording, simplifying complex instructions, or narrowing down the scope to ensure that the prompt is as effective as possible. Optimization often involves making the prompt more specific and reducing ambiguity.
Example: “Write a 300-word summary of the research paper on AI ethics, emphasizing the ethical dilemmas and implications for technology companies.” This version is more optimized than a broad, vague instruction.
5.AI Model Processing:
Once the optimized prompt is provided, the AI model processes it and generates a response. This is where the model applies its underlying machine learning architecture, leveraging its training data to formulate a response.
Example: The AI will analyze the prompt, consider patterns in its training data, and produce a response based on its understanding of the language and context.
6.Generating Output:
The AI model generates the initial output based on the prompt. Depending on the AI model’s capabilities, this output may vary in length, style, accuracy, or even relevance to the task.
Example: If the task was to summarize a paper, the output might include key findings, conclusions, and references to methodology.
7.Output Refinement:
Once the output is generated, prompt engineers review and refine it. This may involve removing irrelevant information, adjusting tone, adding details, or improving clarity. In some cases, the output might need to be restructured to fit the desired format.
Example: If the AI’s response contains tangential information or lacks clarity, the prompt engineer would reword it or fine-tune the output to better align with the user’s expectations.
8.Iterative Improvement:
Finally, the process of prompt engineering is iterative. After refining the output, prompt engineers analyze the effectiveness of the response and assess how the prompt can be improved for future tasks. This leads to continuous improvement, ensuring that future prompts are even more optimized, concise, and aligned with user needs.
Example: The engineer might adjust the prompt for the next interaction to ensure more relevant details or a more focused response.
Key Skills and Tools of a Prompt Engineer
Prompt engineering requires a variety of skills:
Understanding of Language Models:
A prompt engineer should have a deep understanding of how LLMs like GPT process language. Knowing their strengths and weaknesses allows for better prompt design.
Communication Skills:
Effective communication is critical, as prompt engineers must be able to convey complex instructions in a way that the model can interpret clearly.
Creativity and Experimentation:
Crafting effective prompts often requires trial and error, testing different phrasings and structures to see what works best.
Analytical Thinking:
Understanding how different types of inputs influence the model’s outputs and iterating to improve results.
In addition to these skills, prompt engineers also use tools to test and refine their prompts. For instance, platforms like OpenAI’s Playground allow users to experiment with various prompts in real-time, while more advanced professionals might leverage APIs to automate or scale their prompt engineering work.
Best Practices for Prompt Engineering
There are several strategies that a prompt engineer can employ to get the most out of a language model. Below are some of the best practices:
Be Specific and Clear: Ambiguous prompts can confuse AI models, leading to vague or incorrect responses. Make sure the prompt is clear and as specific as possible.
Example: Instead of asking, “Tell me about AI,” a more specific prompt would be, “Can you explain the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning in AI?”
Use Context Effectively: Providing context can guide the model to better understand the desired output.
Example: Instead of saying, “Write a poem,” say, “Write a rhyming poem about the beauty of autumn with a melancholic tone.”
Limit the Scope: Sometimes, less is more. Limit the scope of the prompt to avoid overwhelming the model with too much information or too many instructions.
Example: Instead of “Write an article about the importance of artificial intelligence in modern business, covering all aspects of AI from machine learning to natural language processing,” you could say, “Write a short article explaining the importance of AI in customer service.”
Test and Iterate: A prompt engineer should test various iterations of a prompt to identify the most effective structure.
Give Examples: For tasks requiring specific output formats, include an example to guide the model.
Example: If you want a bulleted list, you could say, “List the steps in a process to build a website. For example: Step 1: Plan the layout.”
Use Temperature and Max Tokens: Some models allow you to adjust the
temperature (which controls randomness)and themax tokens (which sets a character limit)to control the output. These can be adjusted to fine-tune the model’s output.
Comparing with and without Prompt Engineering
Now let’s look at some concrete examples of how a well-crafted prompt versus a poorly constructed one can affect the outcome.
Example 1: Writing a Research Summary
- Without a Prompt Engineer:
Prompt: “Summarize this research paper.”
The AI may generate a generic or overly simplistic summary, without capturing the key aspects of the paper, such as methodology, results, and conclusions.
- With a Prompt Engineer:
Prompt: “Summarize the research paper titled ‘Exploring AI Ethics in Autonomous Vehicles.’ Focus on the methodology, key findings, and implications for policy. Keep the summary under 200 words.”
The AI’s response will be more targeted, concise, and aligned with the user’s expectations, providing a detailed summary that addresses the core aspects of the paper.
Example 2: Writing a Creative Story
- Without a Prompt Engineer:
Prompt: “Write a story.”
The story might lack direction, coherence, or creativity, leading to a generic or even nonsensical narrative.
- With a Prompt Engineer:
Prompt: “Write a short story set in a post-apocalyptic world where humans are living on Mars. The protagonist is a scientist struggling with the ethical implications of using artificial intelligence to terraform the planet. Make the tone introspective and thought-provoking.”
The story produced will be richer, more engaging, and aligned with the specific context and themes the user wanted.
Example 3: Asking for Code
- Without a Prompt Engineer:
Prompt: “Write a Python function.”
The AI may generate a simple function, but it may not meet the user’s needs or lack important features such as error handling or optimization.
- With a Prompt Engineer:
Prompt: “Write a Python function to validate an email address using regular expressions. The function should return True if the email is valid and False if it is invalid. It should also handle common edge cases such as missing domain names or incorrect characters.”
The AI’s response will be much more precise, including the correct implementation, error handling, and edge case considerations.
Conclusion
In the world of AI, a Prompt Engineer plays a critical role in ensuring that AI models deliver optimal results. The expertise of prompt engineers can dramatically influence the quality, relevance, and accuracy of responses from language models like GPT-4. By following best practices—such as being specific, providing context, testing different iterations, and using examples—they can significantly improve the interaction between humans and AI.
As AI continues to evolve, the role of prompt engineering will become even more important, helping users and businesses unlock the full potential of artificial intelligence. Whether it’s writing, problem-solving, or complex technical tasks, the way we interact with AI will increasingly depend on how well we craft our prompts.


