In the world of IoT (Internet of Things), MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a popular lightweight messaging protocol that ensures efficient communication between devices, servers, and clients. MQTT is favored for its low-bandwidth requirements and its ability to work in low network environments. However, testing and debugging MQTT-based applications can be challenging without the right tools.
Today we’re talking about one such tool called MQTTX. MQTTX is a cross platform, open-source MQTT client tool that provides a user-friendly interface for testing and debugging MQTT-based applications. It supports multiple MQTT brokers, including EMQX, Mosquitto, HiveMQ, and others, and provides a range of features such as message history, message filtering, and more. It is available for multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
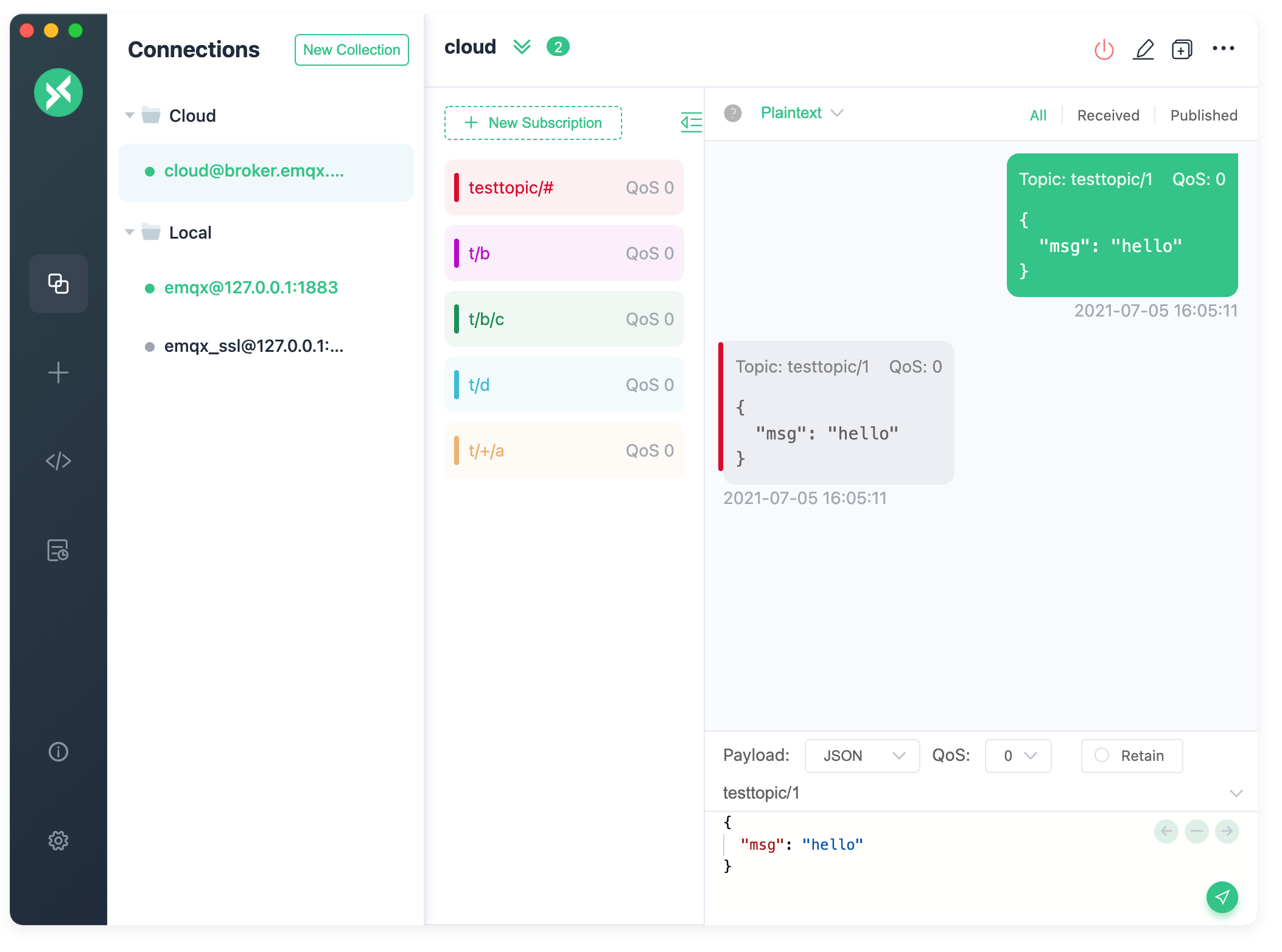
MQTTX supports all versions of the MQTT protocol, from MQTT 3.1.1 to MQTT 5.0, which makes it suitable for a wide range of use cases, from simple applications to advanced IoT systems.
Getting Started
Let’s using MQTTX to test and debug an MQTT-based application. We’ll use the EMQX MQTT broker for this example. And here we using Web version of MQTTX. The web client is https://mqttx.app/web-client.
The public EMQX server information is as follows:
Server: broker.emqx.io
TCP Port: 1883
WebSocket Port: 8083
SSL/TLS Port: 8883
Secure WebSocket Port: 8084
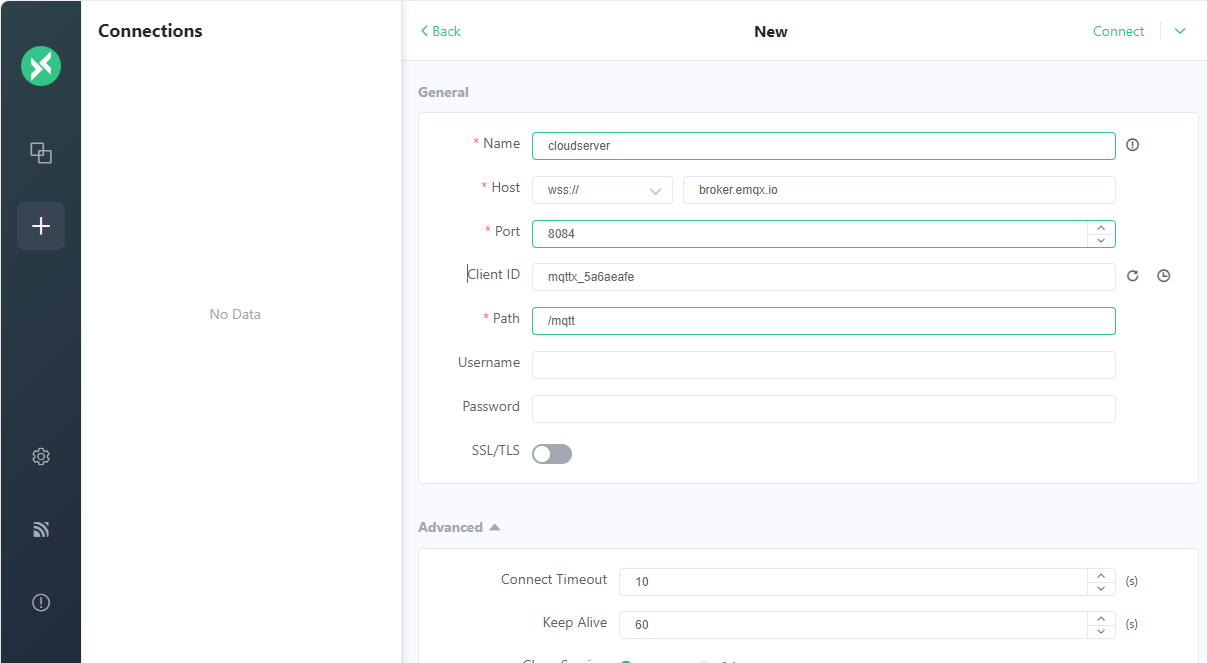
Create a New Connection
Open web client of MQTTX and click on the + button on the top-left corner to create a new connection. Naming the connection as ‘cloudserver’, and keep to using EMQX as the broker.
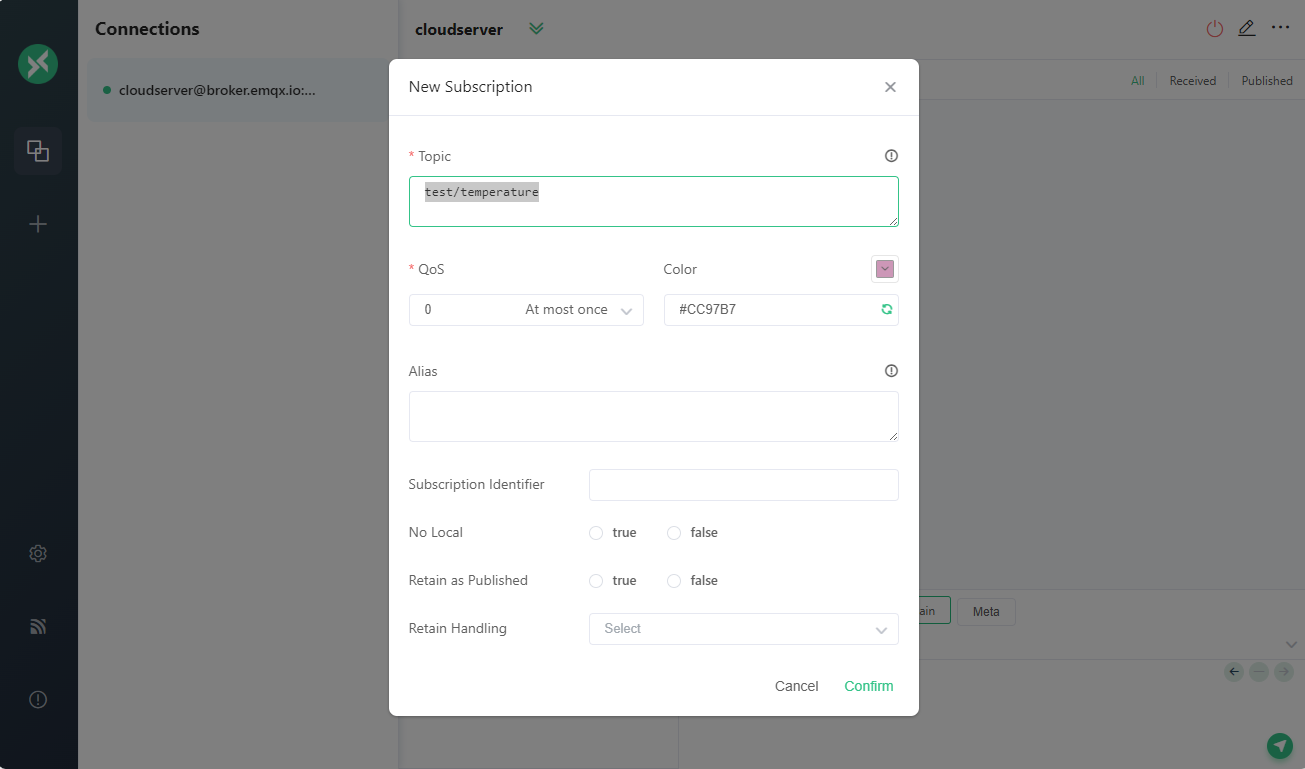
Subscribe to a Topic
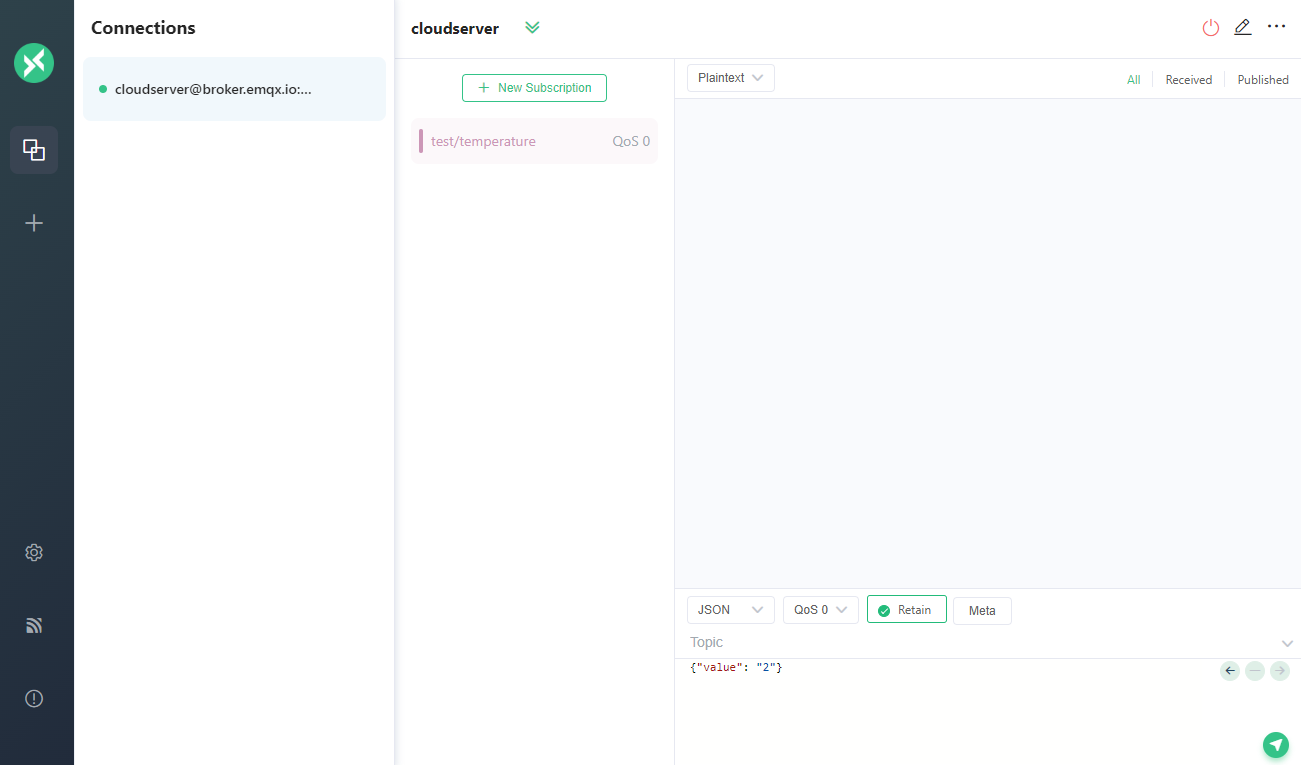
Once the connection is established, we can subscribe to a topic by clicking on the New Subscription button. Let’s subscribe to the topic test/temperature.
Create two new clients
Now, let’s create two new clients connection, naming as sensor1 and sensor2. Both clients will subscribe to the same topic test/resp.
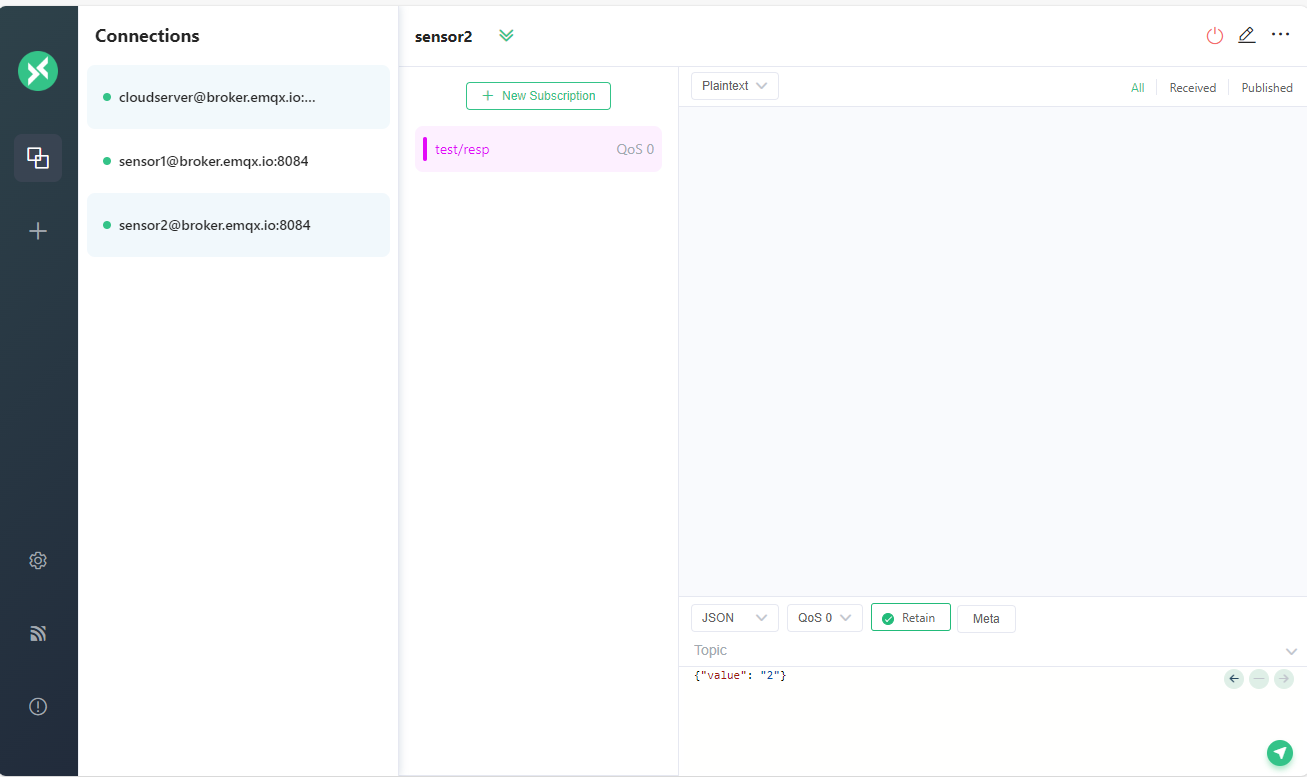
Publish a Message
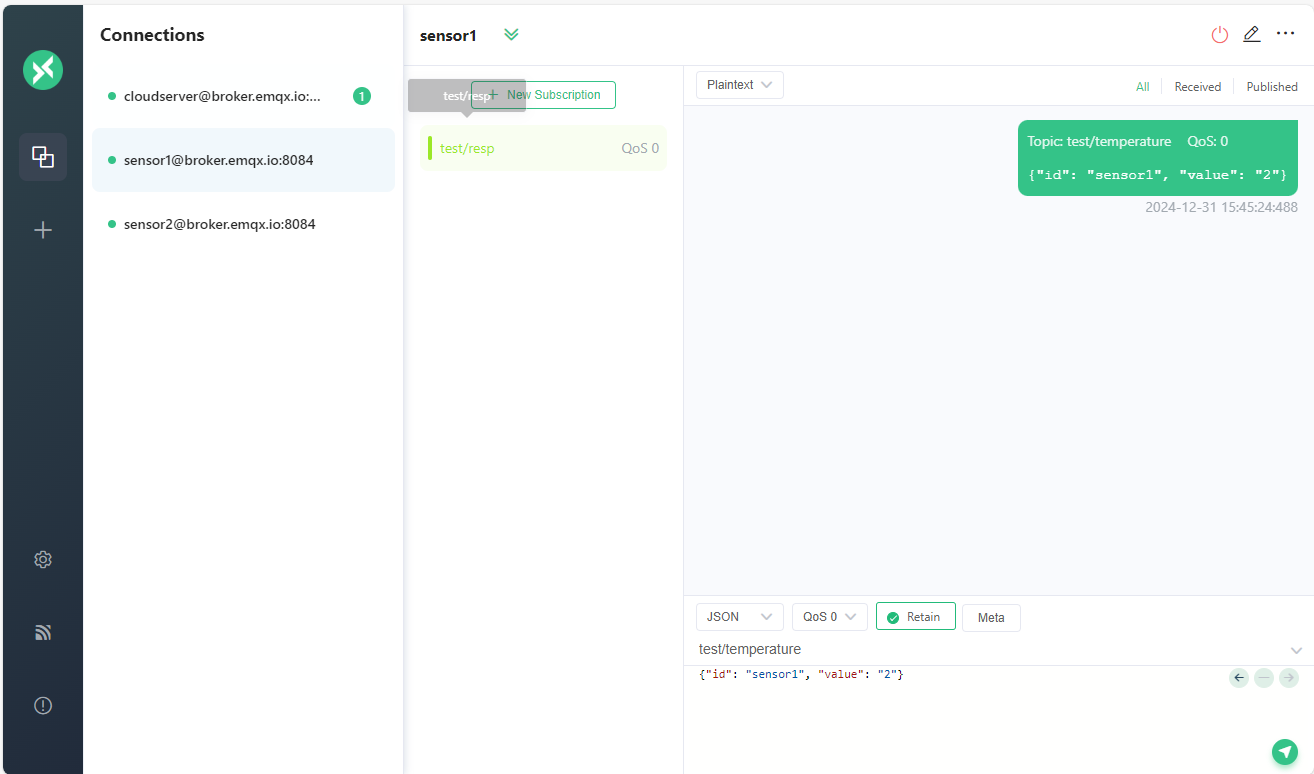
Let’s publish a message which using JSON format from sensor1 to the topic test/temperature. And we can see the message is received by sensor1.
1 | Topic: |
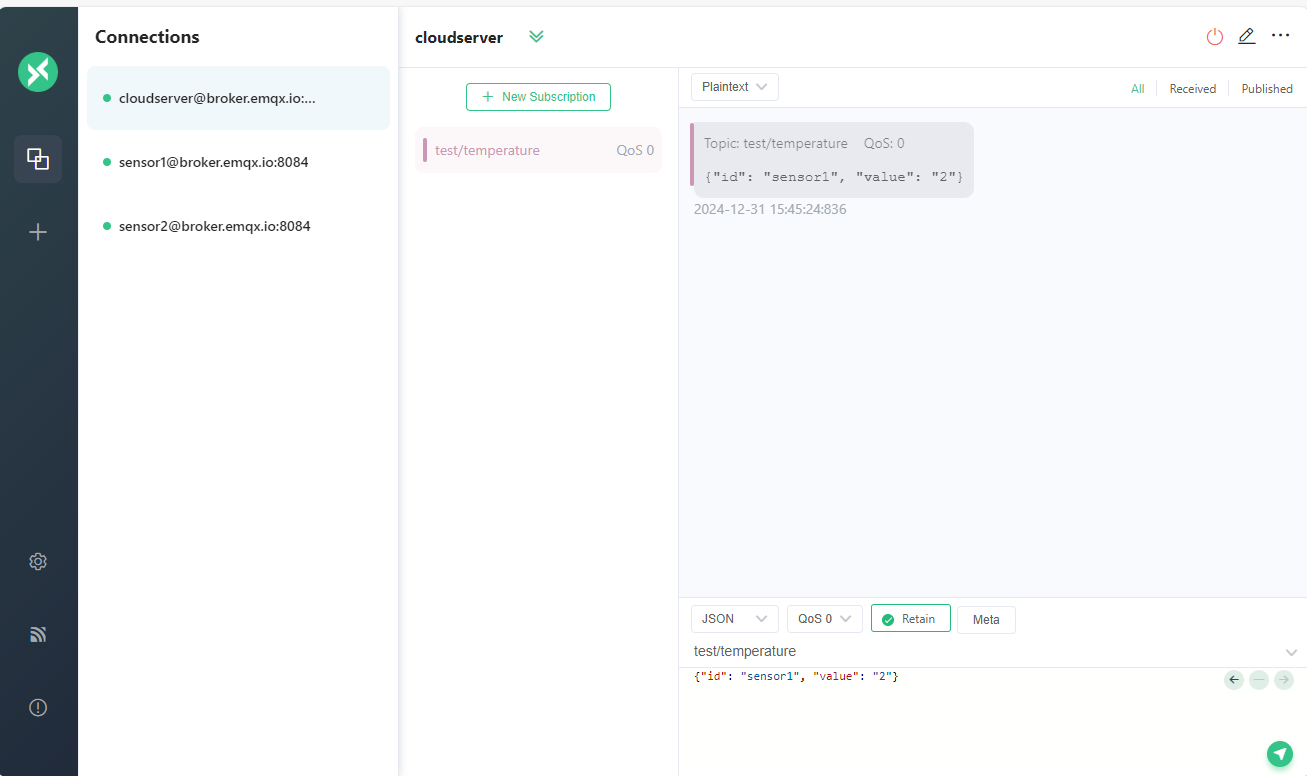
We can see the ‘cloudserver’ client which subscribed the topic test/temperature received the message.
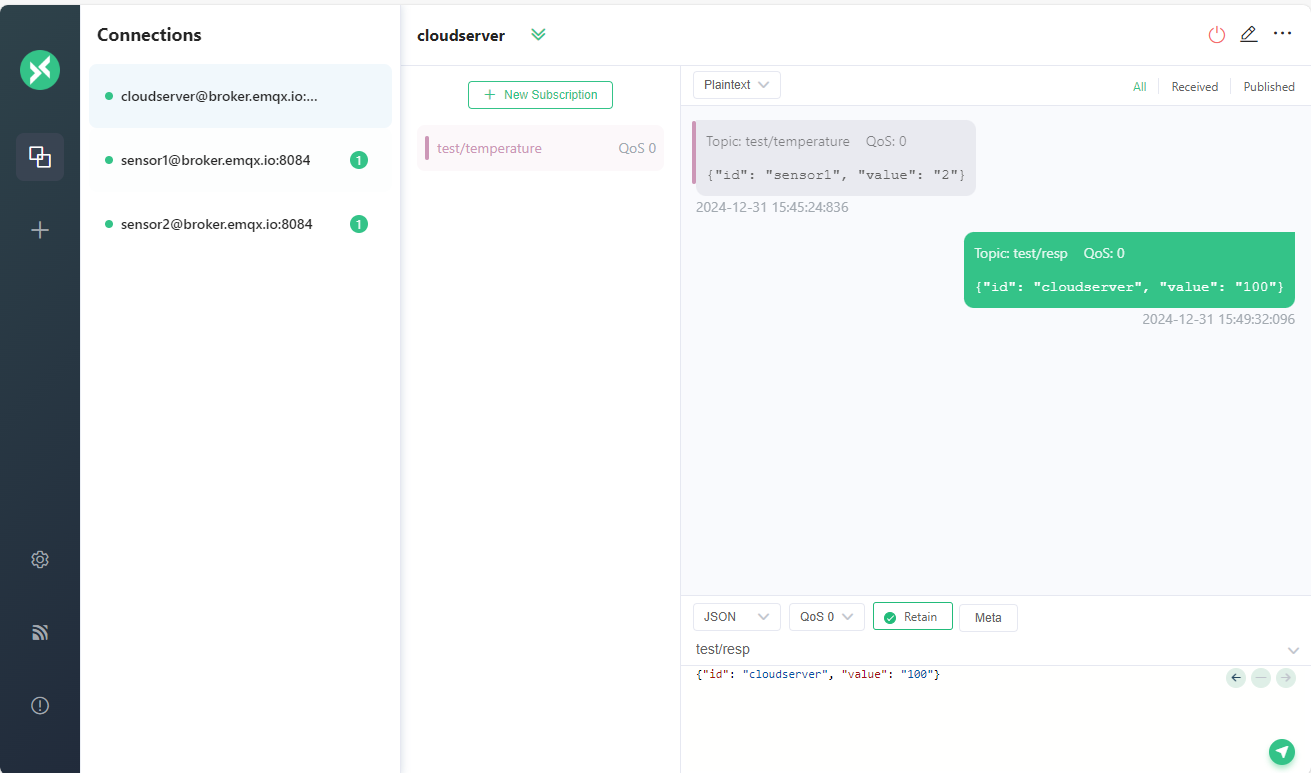
In ‘cloudserver’ client, we also can send the message to the topic test/resp. Then both sensor1 and sensor2 will receive the message.
1 | Topic: |
Topic with Wildcard
The MQTT protocol forwards messages based on the topic. Topics are hierarchical by /, similar to URL paths, for example:
1 | chat/room/1 |
MQTT topics support two wildcards: + and #.
+: Represents a single-layer wildcard, such as A/+ matching A/X or A/Y.
#: Represents a multi-layered wildcard, e.g. A/# matches A/X, A/B/C/D.
Note: Wildcard topics can only be used for subscriptions, not for publishing.
Let’s update the subscription of cloudserver client to subscribe to the topic test/+/temperature. This will match all topics that start with test/ and end with temperature. And using sensor1 client to publish a message to the topic test/1/temperature, sensor2 client to publish a message to the topic test/2/temperature.
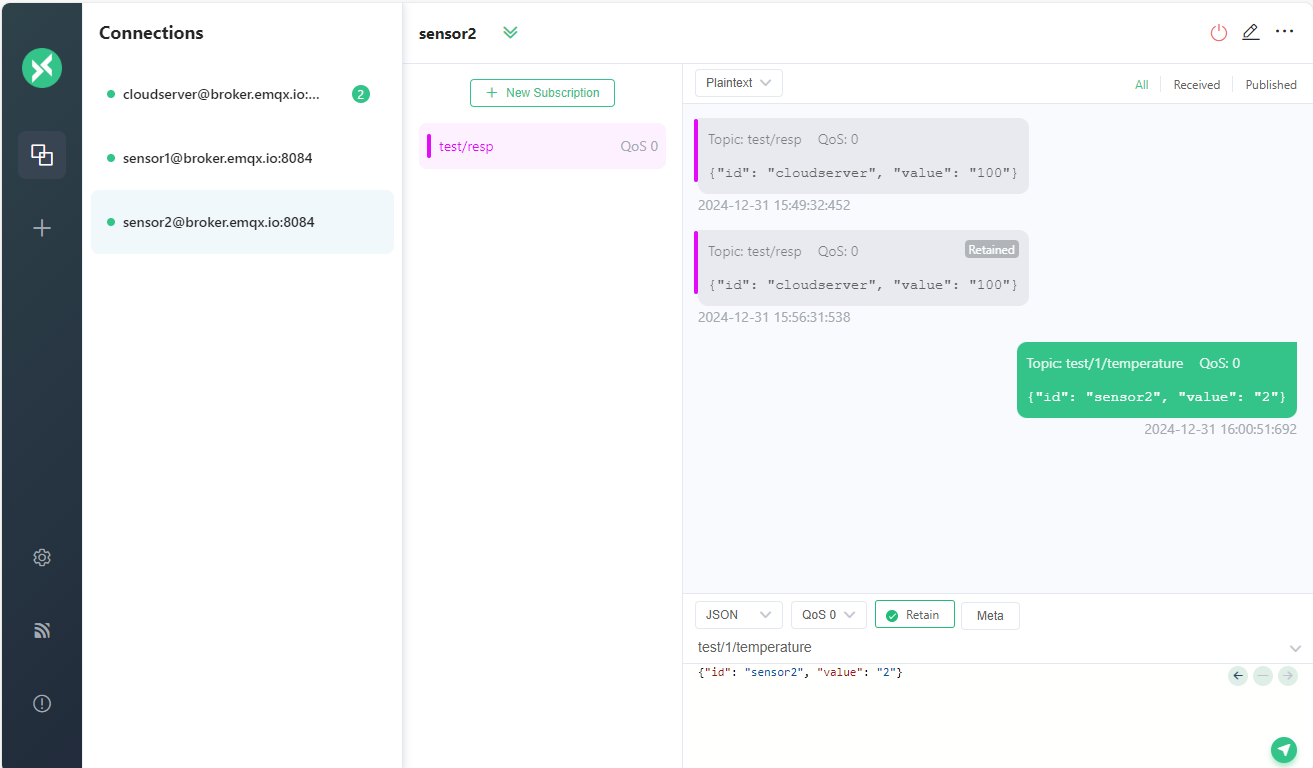
As you can see the cloudserver client received both messages.
The MQTTX tool provides QoS, message retained and more features for testing and debugging MQTT-based applications. You can test and debug your MQTT-based applications using MQTTX.
Client Version
The MQTTX tool client version includes more features such as topic tree visualization.
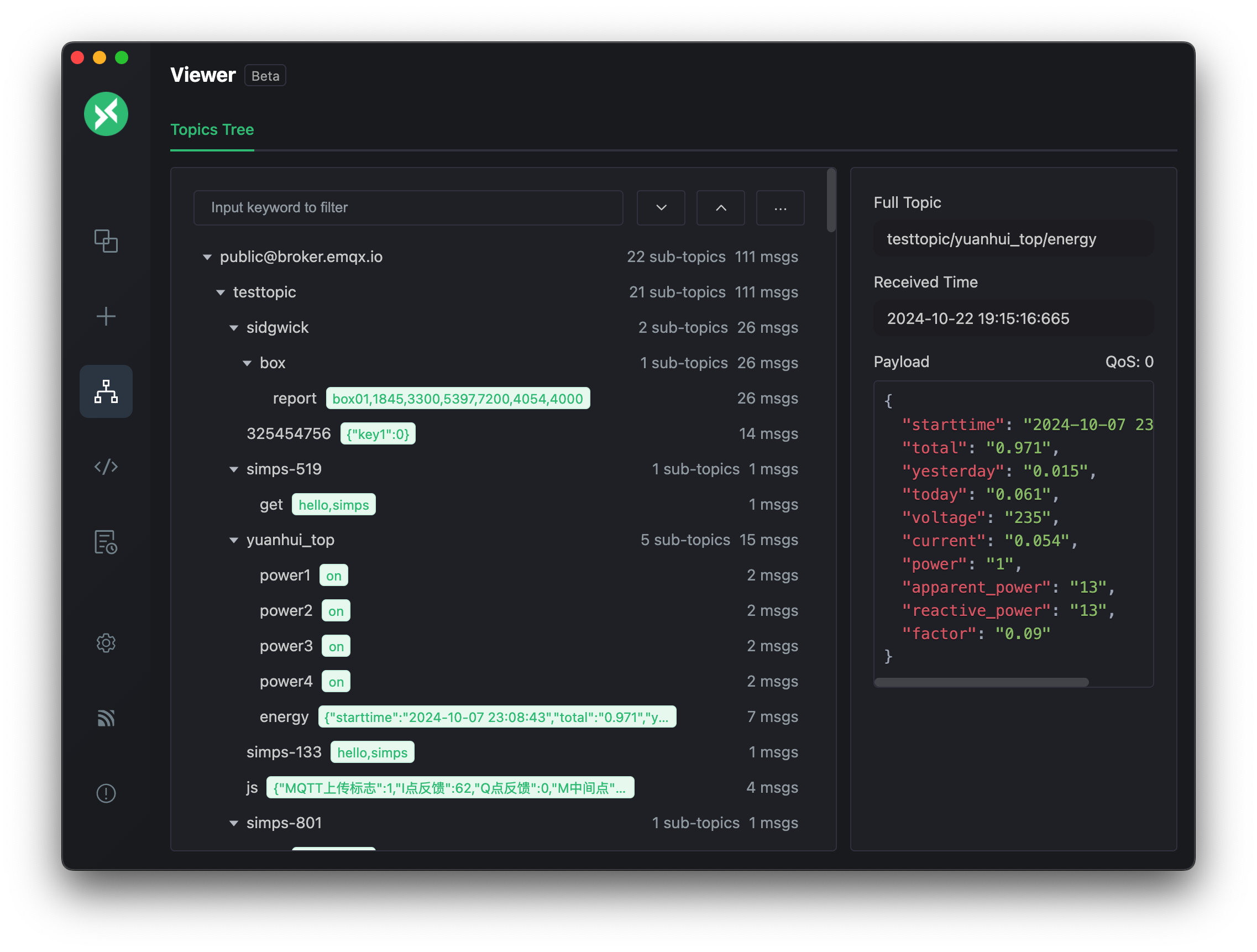
Conclusion
MQTTX is a powerful and user-friendly MQTT client tool that provides a range of features for testing and debugging MQTT-based applications. It supports multiple MQTT brokers, including EMQX, Mosquitto, HiveMQ, and others, and provides a cross-platform client for Windows, macOS, and Linux.


