The entire machine learning domain revolves around data. With clean data, you can gain important business insights. Data enables you to proactively, rather than reactively, make strategic business decisions and helps you gain a deeper understanding of your customers.
The Data Engineering in machine learning refers to the ingest of the data, the process of storing, processing, ETL(extract, transform, load) and analyzing data.
However, storing all this data is challenging. You need a way to store the data in a centralized repository and make it easy to access. This means you need to consider data security, availability, cost, and performance.
AWS provides many services that can help you address these challenges. A data lake is the key solution to address this challenge. With a data lake, you can store both structured and unstructured data.
Data Storage
Data Lake
The AWS Lake Formation and Amazon S3 buckets are the two main components of a data lake. A data lake is a platform for storing and analyzing data, which can help you extract valuable insights.
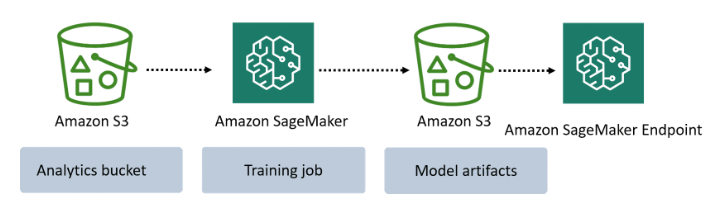
The AWS Lake Formation is the data lake solution provided by AWS, and Amazon S3 is the preferred storage option for data science processing on AWS. Below is a general architecture of a data lake and Amazon S3 for Machine learning.
Amazon S3
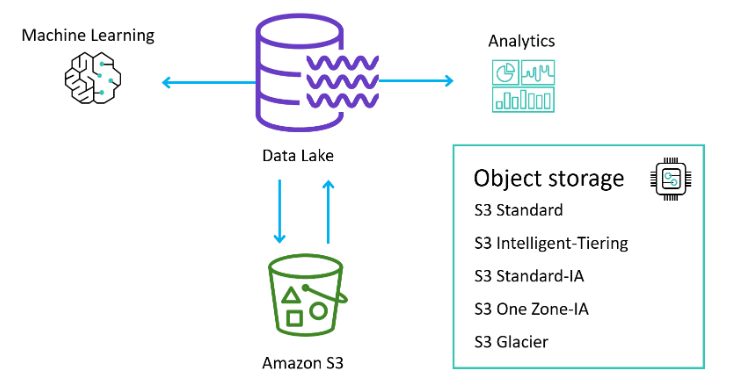
You can use Amazon S3 as storage to store your data. Amazon S3 is a highly available, durable, and scalable object storage service. Amazon S3 offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. It is designed to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere on the web.
There are several storage types of Amazon S3, including:
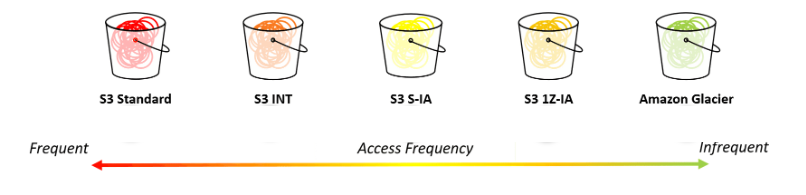
- S3 Standard: This is the default storage class for frequently accessed data. It provides high durability, availability, and performance.
- S3 Intelligent-Tiering: This storage class automatically moves data between two access tiers (frequent and infrequent access) based on changing access patterns.
- S3 Standard-IA: This is a lower-cost storage class for data that is accessed less frequently, but requires rapid access.
- S3 OneZone-IA: This is a lower-cost storage class for data that is accessed less frequently, but requires rapid access. It is designed for applications that require low latency and high throughput.
- S3 Glacier: This is a low-cost storage class for data archiving. It provides retrieval times of
several hours. - S3 Glacier Deep Archive: This is the lowest-cost storage class for data archiving. It provides retrieval times of
several days.
When you train machine learning models using Amazon SageMaker, you can use Amazon S3 to store your training data and model training output. Amazon S3 and Amazon SageMaker integration is used to store training data and model training output.
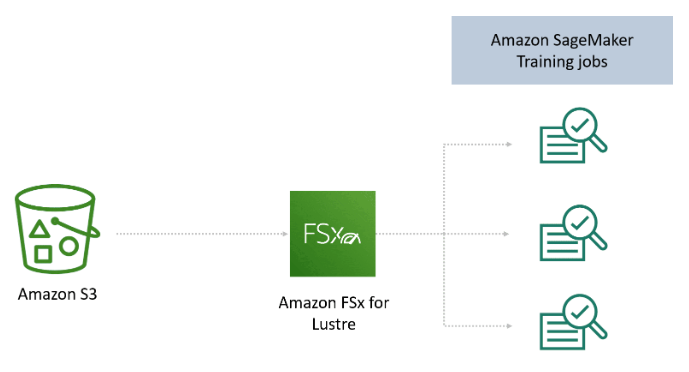
Amazon FSx for Lustre
However, Amazon S3 is not the only storage solution you can use for model training. If your training data is already stored in Amazon S3, and you plan to run multiple training jobs with different algorithms and parameters, consider using Amazon FSx for Lustre (a file system service).
FSx for Lustre provides fast access to Amazon S3 data, which is then provided to Amazon SageMaker. The first time you run a training job, FSx for Lustre automatically copies the data from Amazon S3 and provides it to Amazon SageMaker. You can then use the same Amazon FSx file system for subsequent training job iterations to avoid repeatedly downloading the same Amazon S3 objects.
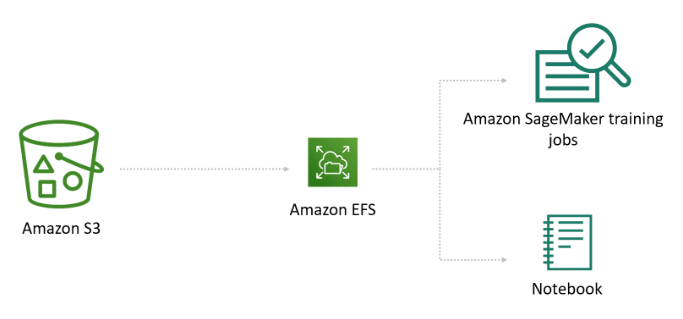
Amazon EFS
Or, if your training data is already stored in Amazon EFS, it may be a good choice as a training data source. The advantage of Amazon EFS is that it can be used to start training jobs directly from the service, without moving the data, resulting in shorter training start times.
If data scientists have a home directory in Amazon EFS, and use it to introduce new data, share data with colleagues, and experiment with different fields or labels in their data set, this advantage is particularly valuable. For example, data scientists can use a Jupyter notebook to clean the training set initially, start a training job from Amazon SageMaker, and then use the notebook to delete a column and restart the training job to compare the results, to see which model performs better.
The Amazon EBS also can be used as a data source for training, but it is generally slower than Amazon S3 and Amazon EFS. Amazon EBS is a block-level storage service that can be attached to EC2 instances. It is ideal for data that is frequently accessed and requires low latency.
Data Ingesting
The Data Ingesting include the batch and streaming data sources.
Batch Data Ingesting
Using batch processing, the data ingestion layer periodically collects source data and groups it, then sends it to Amazon S3 or other target locations. You can group data based on any logical order, activation by certain conditions, or simple timetables. Batch processing is typically used when real-time or nearly real-time data is not required, as it is generally more efficient and cost-effective than other ingestion options.
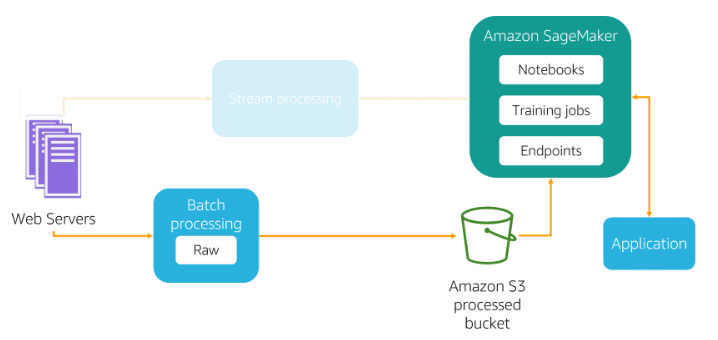
To ingest data in batches to AWS, you can use services such as AWS Glue or Amazon EMR. These are ETL (extract, transform, and load)services that can be used to classify, clean, and enrich data, as well as move data between various data stores.AWS DMSis another service that can help with batch ingestion. It can read historical data from any source system (such as relational database management systems, data warehouses, and NoSQL databases) at any desired interval. You can also useAWS Step Functions` to automate complex ETL workflows involving various tasks.
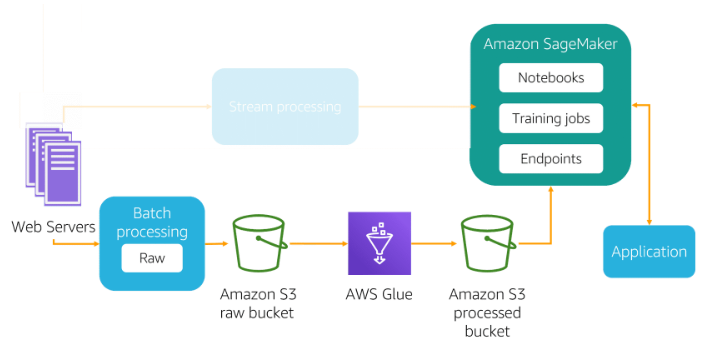
Streaming Data Ingesting
The streaming (including real-time processing) does not involve grouping. Data is created and identified, and it is immediately collected, processed, and loaded by the data ingestion layer. The cost-effectiveness of this ingestion is lower because the system needs to constantly monitor the source and accept new information. However, you may want to use it for real-time predictions (using Amazon SageMaker endpoints that you want to show on your website) or for some real-time analytics that require frequent data refreshes (such as real-time dashboards).
Amazon Kinesis
Amazon Kinesis is a platform for streaming data processing on AWS. It is a fully managed service that can capture and process data in real-time. You can build custom streaming data applications using Amazon Kinesis, which can satisfy your specific needs. It also provides various services that make it easy to load and analyze streaming data.
The Amazon Kineis include several services, including:
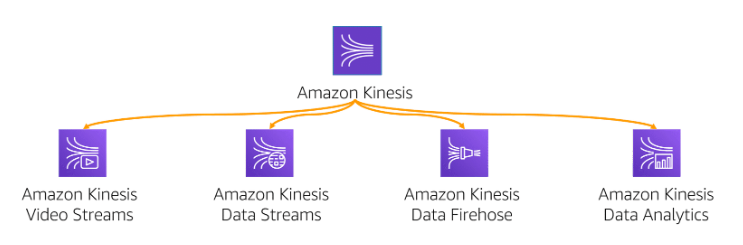
Amazon Kinesis Video Stream: You can use
Amazon Kinesis Video Streamsto capture and analyze video and audio data. For example, a leading home security company uses Kinesis Video Streams to capture audio and video data from its home security cameras. They then connect to their custom machine learning models running in Amazon SageMaker to detect and analyze objects, creating a more comprehensive user experience.Amazon Kinesis Data Streams: You can use
Amazon Kinesis Data Streamsto write data to a stream usingKinesis Producer Library (KPL), which acts as an intermediary between your application code and the Kinesis Data Streams API. You can then useKinesis Client Library (KCL)to build your own applications that preprocess the data as it streams in, and emit data for downstream analysis.Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose: You can use
Amazon Kinesis Data Firehoseto easily batch and compress data as it streams in, and provide an incremental view. You can also use AWS Lambda to perform custom transformation logic before sending the incremental view toAmazon S3.Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics: You can use
Amazon Kinesis Data Analyticsto process and transform data streamed through Kinesis Data Streams or Kinesis Data Firehose usingSQL. This allows you to getnear-real-time insightsfrom the data before it is stored in Amazon S3.
Data Transform and Processing
Ingestion of raw data into services such as Amazon S3 is not directly usable for machine learning. Data needs to be transformed and cleaned, including deduplication of duplicate data, management of incomplete data, and standardization of attributes. If necessary, data transformation may involve changing the data structure to an OLAP model, which makes it easier to query data.
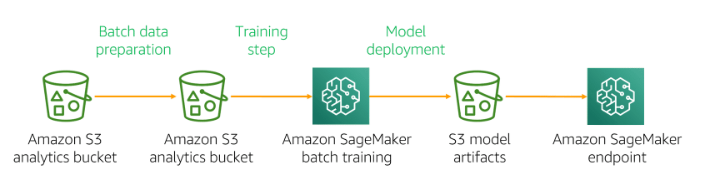
Processing of large datasets typically requires data transformation. Distributed computing frameworks such as MapReduce and Apache Spark can provide protocols for data processing and node task assignment and management. They also use algorithms to split datasets into subsets and distribute them across nodes in the compute cluster. Using Apache Spark on Amazon EMR provides a managed framework that can handle large datasets. Amazon EMR supports several instance types, which have higher CPU and enhanced networking performance, which are ideal for high-performance computing (HPC) applications.
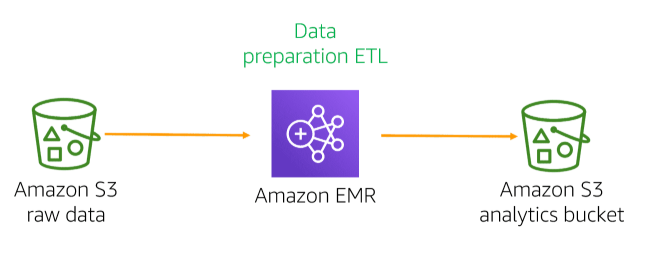
The key step of Machine Learning Data Transformations is to partition the dataset. The Machine Learning application requires dataset from databases, streaming IoT input or centralized data lakes. In many use cases, Amazon S3 can be used as the target endpoint for the training dataset. ETL processing services (Athena, AWS Glue, Amazon Redshift Spectrum) complement each other in functionality, and can be used to preprocess data stored in Amazon S3 or directed to Amazon S3 datasets. In addition to using Athena and Amazon Redshift Spectrum, you can also use AWS Glue-based services to provide metadata discovery and management functionality. The choice of ETL processing tools depends on the type of data you have. For example, if you are processing tabular data using Athena, you can use SQL to process data files stored in Amazon S3. If the compatibility of the dataset or compute with SQL is not the best, you can use AWS Glue to seamlessly run Spark jobs (Scala and Python support) on data stored in Amazon S3 buckets.
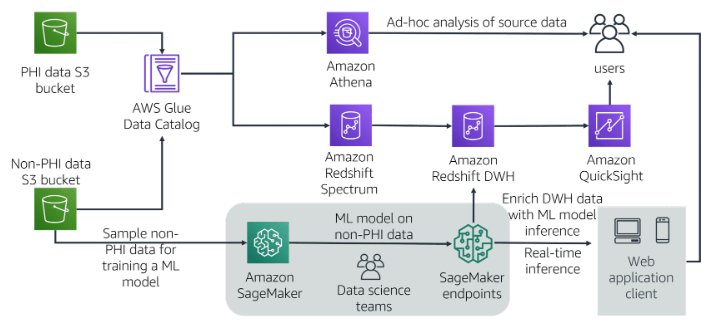
Below is an example architecture for a medical data lake and analytics layer on AWS. This reference architecture demonstrates how AWS services for big data and machine learning can help build a scalable analytics layer for healthcare data. Customers can store a single data source in Amazon S3 and use Athena for ad-hoc analysis; integrate with data warehouses on Amazon Redshift; build metrics visual dashboards with Amazon QuickSight; and build machine learning models with Amazon SageMaker to predict readmission rates. Users can connect to the data without moving it and use different services to access the data, thus avoiding the creation of redundant copies of the same data.